How To Use Ipv6 In Browser
Your browser is avoiding IPv6.
- What we found What causes a preference for IPv4 Why this worries united states of america
This document explains why we worry when IPv4 is preferred over IPv6.
What we found
This section applies only when we offered to show you this folio from inside the exam.
Outset of all, we detected you lot had a working IPv6 connection. Nosotros also establish that your IPv6 connexion, was using a "real" IPv6 address; meaning not a Teredo or a 6to4 address.
Second, we detected that when given the choice, your browser decided information technology would adopt to employ IPv4 instead of IPv6. This has some concerns for united states of america.
Causes for preferring IPv4
There are several possible reasons why a browser might adopt IPv4 instead of IPv6.
- Google's "Chrome" has a "fast fallback" mechanism. On the first try to a site, it will prefer IPv6. If connections take longer than a third of a second, IPv4 is attempted in parallel; and the better of the two will be used for that site. (more than info)
- Firefox (recent builds) does the same equally Chrome. (more info)
- Since Windows 7, the operating system volition periodically examination to see if IPv6 works. If the health check fails, then many applications (including Internet Explorer) will employ IPv4, to insulate you from any local IPv6 misconfiguration. (more info)
- Apple's Lion and Mountain Lion updates will prefer whichever is "faster" for a given destination. As of Bone X 10.eleven "El Capitan" and iOS 9, IPv6 is given a slight preference; but will fall back to IPv4 if network conditions warrant information technology. (more info)
Why this worries the states
When you employ the Internet, a connection is made between your computer, and the service yous're connecting to. To connect, you have to have the other side's IP - Net Protocol - number. And, when y'all connect, they see yours, and so they tin send traffic dorsum to you and your applications.
The Net protocol that we've been using for the 1990'southward and the 2000s, has run out of these unique numbers. Nosotros can proceed going, merely with some limitations, by sharing multiple machines with one number. Oft times, we do this at home or at work.
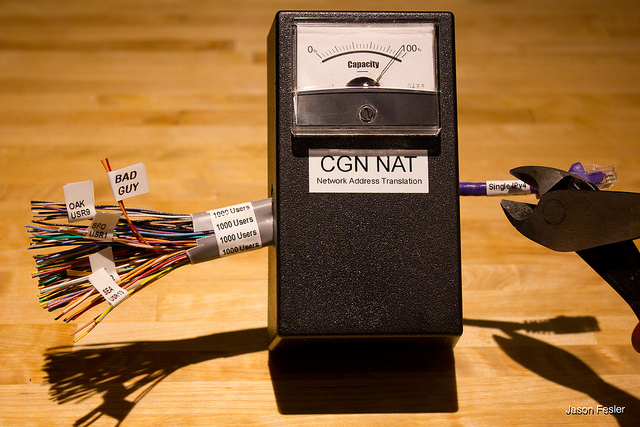
What is changing is that the Internet Service Providers are all facing the fact that they will have to implement this blazon of address sharing, on a much larger scale. Some buzzwords you may hear: NAT, CGN, Carrier Grade NAT, LSN, Large Scale NAT. They all wait something like this:
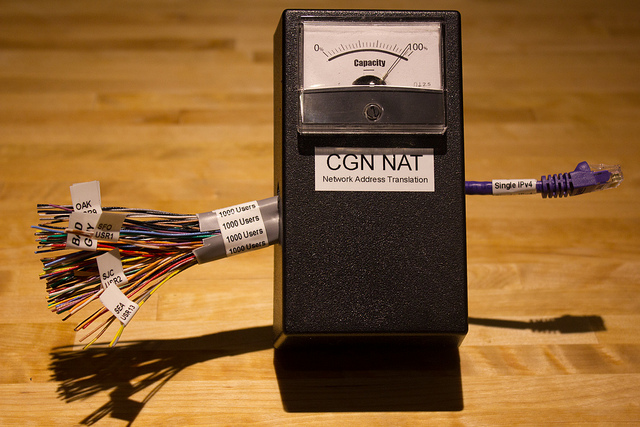

Photo by Jason Fesler - http://flic.kr/p/bhDoxg
The thing to watch for here: Many houses sharing one public address.
What happens if i of those homes has a bored hacker, or (more probable) a compromised auto owned by someone who doesn't stay upwards to date, and doesn't run antivirus software? What happens when that machine starts to attack your favorite web sites? What nearly your banking site?
Those sites will take to ultimately protect themselves, past blocking the traffic. Unfortuantely, they but run into the shared accost, so their blocking information technology looks like this:
Photograph by Jason Fesler - http://flic.kr/p/bhDomR
This is not a good state of affairs. And the main way to avoid it, is to make sure that your IPv6 is working; and to brand certain that IPv6 is the preferred protocol.
Most OS's and Browsers will automatically have a strong bias towards a working IPv6 connection instead of the (perhaps shared address) IPv4 connectedness. If yours does not, and you want to run across this changed, let the browser company know. You might as well find other browsers on the same Os will piece of work the way you'd expect, if y'all need a work-around.
Why else should I care about IPv4 beingness preferred instead of IPv6, when I have both available?
- Sites that decide your location automatically, will get this wrong more frequently when you share an IPv4 address with people in other cities.
- The box that shares an accost between you and the other hundreds of houses, may become functioning constrained (cpu, network, TCP ports)
- The box is a potential central point of failure for your internet access
- Sharing IPv4 addresses is an extra expense for the ISP that they will be passing on to their customers
Copyright (C) 2010, 2022 Jason Fesler. All rights reserved. Version 1.1.932 (23f496c)
Mirrors | Source | Email - - Attributions | ![]() en_US
en_US
This is a mirror of test-ipv6.com. The views expressed here may or may non reflect the views of the mirror owner.
How To Use Ipv6 In Browser,
Source: https://test-ipv6.com/faq_avoids_ipv6.html
Posted by: hertzogdair1985.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Use Ipv6 In Browser"
Post a Comment