How To Read A Mold Test Report
Mold Testing – Air Quality Lab Interpretation

Mold Testing Air Quality Lab Interpretation
People with asthma and mold allergies are the commencement to ask about mold testing. Since their symptoms are primarily respiratory, it is only logical they inquire for "air quality testing." Other individuals looking for peace of mind or suffering much more severe symptoms sometimes besides ask for mold testing air quality services. This blog is almost air quality testing and some of the variables and limitations that should be considered in every mold testing chore.
Part of our chore is to help develop a mold testing air quality sampling program specific to your project, and to help interpret the lab results in light of discoveries made during the visual inspection. I've heard mold testing described as "an art and a science," and I agree with that sentiment. Since it's not a federally regulated contaminant it has been a picayune bit of the wild westward in terms of who tests, what they examination for, and how the results are interpreted. For a client – that should scare you lot! – because it has meant that anyone could call themselves mold inspectors without having acceptable grooming or professional credentials to demonstrate their competence.
Mold Testing – When to Exam Air Quality?
Most experts, including the EPA and California Department of Public Health, suggest just testing nether very specific weather condition. In full general, a moisture and mold inspection by a qualified professional person is far more useful in determining if a mold problem exists. However, at that place are some circumstances that warrant additional air quality testing. The most commonly referred to guidance for how to perform mold inspections and when/how to examination for mold is the AIHA "Green Book," Recognition, Evaluation and Control of Indoor Mold.

Mold Testing AIHA Light-green Volume
Here are three full general reasons that justify mold testing:
1) Determining the scope of contamination.
2) Determine the blazon of contamination.
3) Clearance testing.
Mold Testing – What Type of Air Quality Testing Method?
If mold testing is pursued, these are the three most common types of samples nerveless:
- Air sampling: the most common form of sampling to assess the level of mold. Sampling of the inside and outdoor air is conducted and the results to the level of mold spores within the bounds and exterior are compared. Oftentimes, air sampling will provide positive identification of the beingness of non-visible mold.
- Surface samples: sampling the amount of mold spores deposited on indoor surfaces (record, and dust samples). Dr. Ritchie Shoemaker, Md is a strong believer in dust sampling using the Ecology Relative Moldiness Alphabetize (ERMI).
- Majority samples: the removal of materials from the contaminated surface area to identify and determine the concentration of mold in the sample.
In this weblog, we focus on air quality testing. There are four ways of air quality testing for mold:
- Spore trap not-viable (non-culturable) sampling. While controversial, this is the virtually common type of "mold testing" nosotros see performed in the industry. A calibrated pump draws a known volume of air over a greased slide. This is an "impaction" method of collecting spores. Based on a directly microscopic examination of a portion of the slide, the lab extrapolates how many spores are nowadays per cubic meter, and can place many common genera of mold. One weakness of direct visual examination is that some common genera, such as Penicillium and Aspergillus, cannot be differentiated and reported cumulatively. Another obvious weakness is that heavier spores, such as Stachybotrys, may be present just not aerosolized and therefore underreported if only air sampling is performed.

 Mold Testing Air Quality Testing – Alex Stadtner using pump and Sporetrap
Mold Testing Air Quality Testing – Alex Stadtner using pump and Sporetrap - Pitri Dish-style, viable (culturable) sampling. The 2nd most common type of air sampling for mold is also an impaction-mode collector. A petri dish with a growing media is placed beneath a pin-holed cap and air is drawn over the petri-dish. The petri-dish is so incubated and visually inspected so the number of colony forming units (CFUs) of different types of molds are identified and counted. Mutual types of mold growth media are Malt Extract Agar (MEA), Potato Dextrose Agar (PDA), and Hay Infusion Agar. A forcefulness of this method is that molds tin be especiated. So in improver to differentiating betwixt genera similar Penicillium and Aspergillus, using viable (culturable) analysis you can place if the mold is Aspergillus niger, or Penicillium marneffei. This can exist valuable information since there are hundreds of species within each genera, and some are more toxigenic than others. Some weakness of this sampling method include the fact that unlike molds prefer different growth media, temperatures and moisture levels, but the lab volition just use a "standard setting" unless instructed otherwise. So to get a more complete picture of the viable airborne spores in one infinite y'all may need to collect numerous petri-dish samples using different agars and to be incubated under different growing conditions. Some molds grow well under lab conditions, and others don't. Some molds produce powerful chemical weapons used against neighboring colonies, which tin influence the number of CFUs counted for both species.
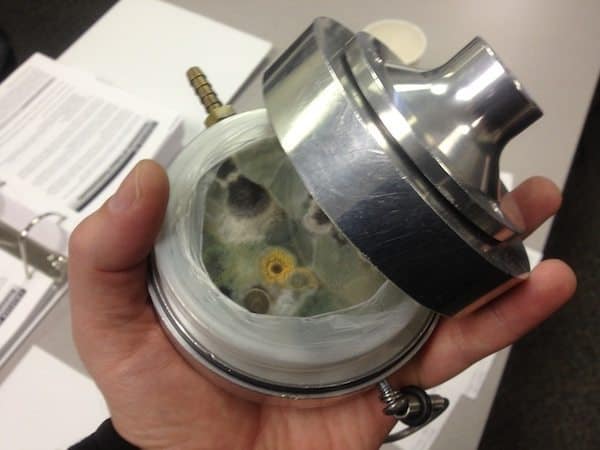

Mold Testing Petri Dish Impactor
- Microbial Volatile Organic Compound (MVOC) sampling. When molds are moisture and have food they grow. When mold is "eating" information technology produces metabolic byproduct gases known equally MVOCs. Air samples can either be collected in a summa canister or sorbent tube, and the lab analyzes the air sample for a limited ready of microbial VOCs. MVOC indicator gases include but are non limited to the post-obit: Furan, 1- and 2-Pentanol, 2-Hexanone, ii-Heptanone, 1- and 3-Octanol, and Geosmin. Most MVOC scans are limited in that they do not clarify for every possible MVOC, and most MVOCs have not been directly tied to a single species of mold so extrapolating from only MVOC information is rather limiting. If you scent "musty" odors y'all are probably inhaling MVOCs. It'south a sign of active microbial growth and can be tested via air sampling.
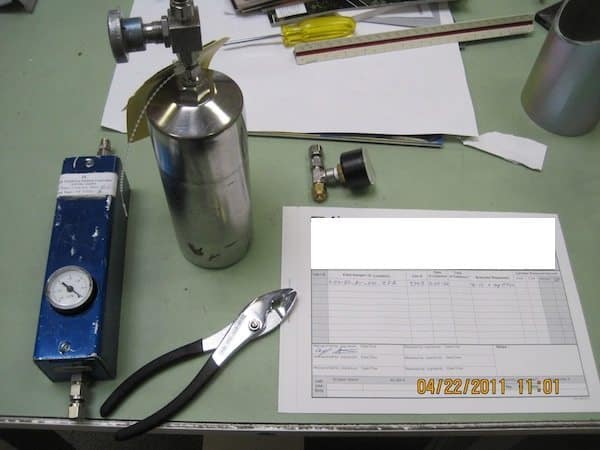

MVOC Testing for Mold

MVOC Mold Testing with Sorbent Tube or Summa Canister
- Mycotoxin Testing. Mycotoxins are secondary metabolites produced by fungi. These are basically self-produced chemical weapons wich can damage other mucus, and can also cause disease and death in humans. Although the primary concern for humans is for ingestion, inhalation is as well of concern. Few indoor environmental consultants are currently testing for mycotoxins. The three most commonly analyzed mycotoxins include aflatoxin, trichothecenes, and ochratoxin. The lab utilizes polymerase concatenation reaction (PRC) assay to identify and quantify mycotoxins in air samples. Samples are nerveless in 37mm cassettes, preloaded with 0.45 um pore-sized filters, and sampling times are longer than typical sporetrap grab samples. Whereas the to a higher place referenced types of lab assay rely on a lab technician's ability to visually identify and count… PCR has over a 95% confidence rate and is more automated.
Mold Testing – How to Interpret Lab Results and Air Quality Information?
Then you've had an inspection and received the lab results… what does it all mean? Companies that only transport convoluted lab reports without further explanation should be put out of business. It is the office of the Certified Indoor Environmental Professional to aid interpret the lab results in combination with what was gleaned from the visual inspection.
Sporetrap lab results should include, at the VERY minimum, ane outdoor sample and a handful of indoor samples. The outdoor sample is used as a control to compare to the indoor samples. Because there tin be such variation in sporetrap samples the statistical significance from collecting so few samples is very limited. Most labs simply share a nautical chart showing how many of which blazon of genera were present.
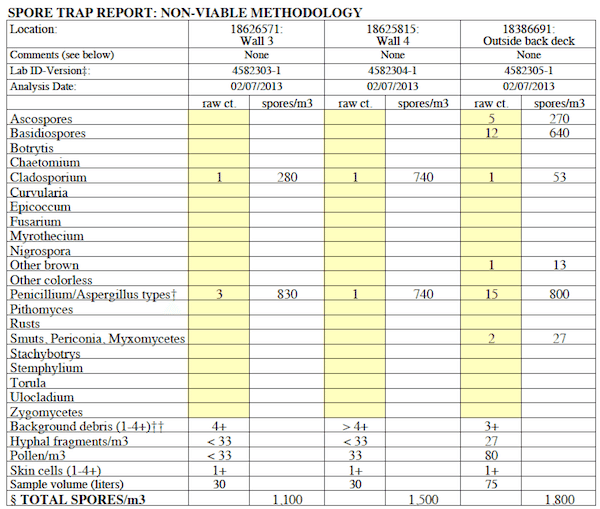
Sporetrap Nautical chart – Mold Testing Non-Feasible, Non-Culturable
Some labs offer their ain "limited interpretation," such as the MoldScore from EMLab P&G. "MoldSCORE™ is a specialized method for examining air sampling data. It is a score betwixt 100 and 300, with 100 indicating a greater likelihood that the airborne indoor spores originated from the outside, and 300 indicating a greater likelihood that they originated from an inside source…" Below you can see some obvious "spikes" that EMLab identified every bit statistically significant higher counts of Cladosporium and Pen/Asp indoors compared to outdoors.
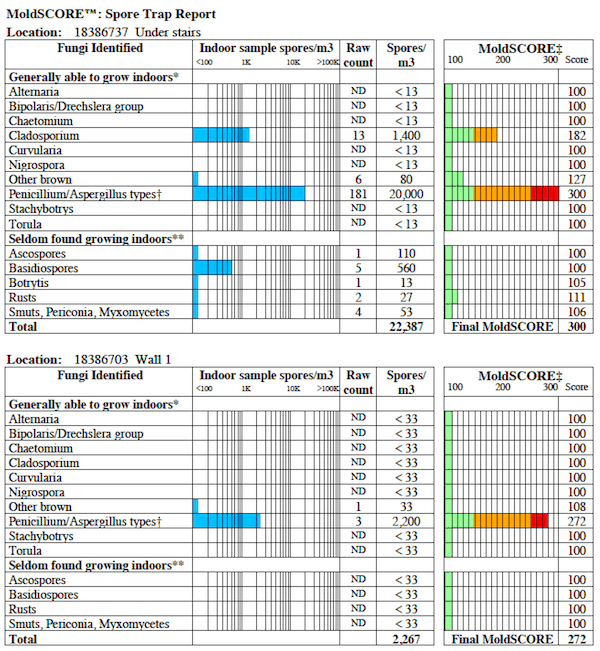
Mold Testing Lab Estimation
Some Building Biologists refer back to the Good for you Dwelling house Standard for guidance on interpreting sporetrap results:

Building Biology Sporetrap Estimation Method
Viable (Culturable) results are usually presented in CFU'due south, and different labs use dissimilar set points to determine low, medium or high probability of significant mold growth. Building Biologists often refer to the Healthy Home Standard suggested interpretation guidelines:

Building Biology Viable Culturable Lab Estimation
There is much less standardization for interpreting these concluding 2 sample types. MVOC results may come with lab estimation such every bit this: "Levels beneath 8 ng/L are typical for most homes and should non crusade groovy business concern for salubrious individuals. Levels betwixt 8 and thirty ng/Fifty bespeak a low level of mold which, generally, affects people who are sensitive to molds. Levels above 150 ng/L point that a high level of active mold growth is present and it is likely that most all occupants of the home will be affected."
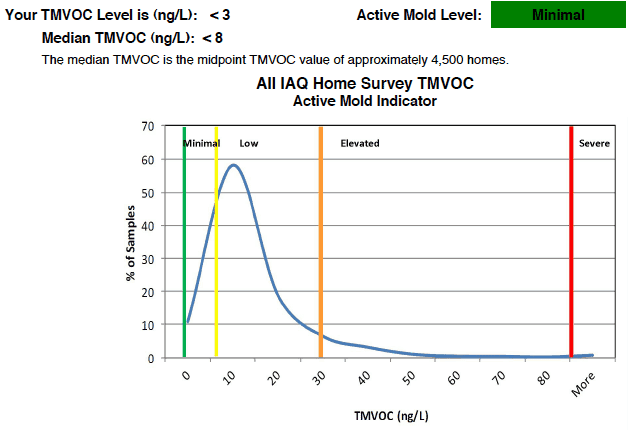
Microbial VOC (MVOC) Lab Assay
Mycotoxin results may be paired with an private'southward claret test results, if they are working with an environmental doctor. We are often called in as a result of an ecology medicine practitioner finding that an individual'due south trunk is reacting to mycotoxins… and so we take to observe where that exposure is occurring – usually at home or work.
1) Decide if ecology sampling would add value to the case, 2) define a sampling plan that would answer a question or prove/disprove a hypothesis, 3) perform testing in accord with industry guidelines, 4) only use qualified laboratories with good track records and the advisable certifications, 5) interpret data in combination with information collected during the inspection, half dozen) provide the interpretation in a user-friendly style written to the "correct audience."
Until mold testing becomes more regulated information technology will remain "an fine art and a scientific discipline."
Healthy Building Science is an environmental consulting house which provides mold testing and mold inspection services for commercial, residential, multi-family unit, buildings, offices, industrial and manufacturing workplaces, hospitals and medical facilities, and single-family homes in the greater San Francisco Bay Area and all of Northern California including the cities of San Francisco, San Jose, Oakland, and Sacramento.
Source: https://healthybuildingscience.com/2013/02/14/mold-testing-air-quality/

0 Response to "How To Read A Mold Test Report"
Post a Comment